¿What is the purpose of a Barcode?
Since 1973, barcodes have become a global standard driving efficiency, traceability, and digital transformation in companies.
What is a barcode
A barcode is a graphical representation of numeric or alphanumeric data, such as GTIN (Global Trade Item Number) or GLN (Global Location Number). These identifiers allow companies to automatically and uniquely recognize, read, and distinguish products, packages, pallets, or locations anywhere in the world.
When scanned, the code transmits key information about the associated product, facilitating inventory management, traceability, and the integration of information with ERP systems and IT platforms.
The GS1 barcodes have become a universal language for the supply chain, enabling global organizations to operate with greater efficiency, security, and data accuracy. Since their first implementation in 1973, they have marked a turning point in process automation and digital transformation of companies, particularly in large-scale retail.
The first scan of a GS1 barcode took place on June 26, 1974, at a Marsh supermarket in Ohio (USA), when a pack of Wrigley’s Juicy Fruit gum was scanned using a UPC reader. This historic event marked the beginning of retail automation and laid the foundation for global traceability in the supply chain, establishing the barcode as a universal standard for product identification
EDI solutions for the supply chain
Complete automation and integration with all your trading partners from a single EDI communications platform.
Global regulation: GS1 General Specifications
All GS1 barcodes are governed by the GS1 General Specifications, an international standard that defines:
- How to generate barcodes with identifiers such as GTIN, GLN, and SSCC.
- Rules for printing, sizing, and placement on packaging and containers.
- Quality requirements and universal readability on any scanner.
Thanks to these specifications, a GS1 bar code works the same way in any country or sector, consolidating itself as a common supply chain language that guarantees interoperability, compliance, and global traceability.
Difference between codes: GTIN-13, GTIN-14, and GS1-128
GTIN-13 → EAN-13
This is the most widely used code in retail. It applies to consumer products and allows them to be recognized at any point of sale worldwide.
GTIN-14 → ITF-14
The GTIN -14 is used to identify groupings of products, such as boxes or shipping cartons. It is more robust, with thicker lines that facilitate reading in logistics environments and ensure traceability during storage and transport.
GS1-128
This is the standard for logistics units (pallets, shipping boxes, deliveries). Although not scanned at the point of sale, it is essential in warehouses and global supply chains. It allows additional information such as batches, expiration dates, or serial numbers to be added, strengthening traceability and inventory control.
Technical aspects of GS1 barcodes
Although different types of barcodes exist, they all share basic technical rules that ensure they work properly when scanned anywhere in the world:
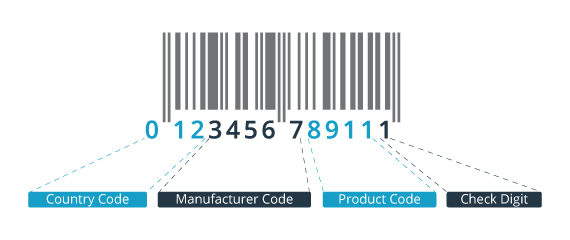
- Check digit: all GTINs include a mathematically calculated number that verifies the code has been read or entered correctly.
- Size and placement: the GS1 General Specifications indicate the minimum and maximum symbol size. They also specify where it should be placed on packaging so that scanning is quick and accurate.
- Human-readable text (HRI): the number associated with the symbol is printed below it so that it can also be read without a scanner if needed.
- Print quality and verification: the codes must be printed with sufficient contrast and sharpness so they can be reliably read throughout the supply chain. Verification tests exist to ensure they meet these requirements.
- Scanner compatibility: GS1 barcodes are designed to be read by standard equipment in any country, ensuring global interoperability.
Anatomy of an EAN-13 barcode
GS1 Digital Link: the bridge between the barcode and the digital experience
The GS1 Digital Link is the standard that expands the role of barcodes in the digital age. Previously, identifiers like GTIN, SSCC or GLN were internal keys used in management systems. Today, the Digital Link converts them into unique URIs that can be read on the web, directly connecting the physical product with digital information in real time.
Strategic benefits for companies
Consumer experience. A single code can direct users to specific pages depending on language, location, or device. Example: a consumer in Germany scans a product and receives nutritional information in German, while another in Mexico accesses the same product sheet in Spanish.
Traceability and compliance. The Digital Link enhances traceability and regulatory compliance by including attributes such as batch, expiration date, or unique serial number. This ensures stronger regulatory control and easier integration with EPCIS 2.0 platforms.
Centralized management with resolvers. The standard allows the use of resolvers. These are services that read a URI (a unique address) and redirect to the corresponding resource: technical sheet, user manual, loyalty app, or regulatory information. This provides flexibility without needing to change the printed code.
Other types of GS1 barcodes: linear and two-dimensional
The current content focuses on EAN-13, ITF-14 y GS1-128, which are the most widely used in retail and logistics. However, the GS1 system includes additional symbologies that are essential for providing a complete international perspective.
Additional linear codes
UPC (Universal Product Code): standard in North America, equivalent to EAN-13 in Europe and Asia. It was the first code scanned in a supermarket in 1974 and remains the retail standard in the United States and Canada.
GS1 DataBar: more compact, designed for small or fresh products (fruits, vegetables, pharmaceuticals). It allows additional data such as weight or expiration date, improving inventory management precision.
Códigos 2D: the evolution of the barcode
GS1 DataMatrix: a two-dimensional code that stores large amounts of data in a small space. It is the standard in industries with high traceability and compliance requirements, such as healthcare, automotive, and medical devices. It strengthens consumer safety and risk management.
GS1 QR Code: connects the physical product with digital information in real time through the GS1 Digital Link. In addition to improving traceability in the supply chain, it enhances consumer interaction, by offering details on origin, instructions, sustainability, or promotions.
These 2D codes represent a shift toward a more digital and transparent value chain. A single symbol can support logistics, compliance, and customer experience.
Strategic advantages of using GS1 barcodes
The adoption of GS1 barcodes provides tangible benefits for global companies, directly impacting operational efficiency, safety, and traceability:
Immediate data capture: eliminates manual processes and accelerates decision-making.
Error reduction: prevents data entry mistakes, ensuring higher accuracy in accounting, logistics, and inventory systems.
Counterfeit prevention: strengthens product authenticity and protects the brand.
Consumer safety: facilitates the identification of batches and expiration dates, enabling defective products to be withdrawn quickly.
Process efficiency and optimization: streamlines communication between business partners and improves supply chain synchronization.
Standardized information classification: ensures data is managed consistently across local and international environments.
Shipment and inventory management: enables precise control of receipts, stocks, and real-time logistics traceability.
Key uses of GS1 barcodes in strategic sectors
Healthcare
Unique patient identification: links relevant information to improve safety in treatments and diagnoses.
Management and traceability of medical devices: ensures control of inventories, batches, and expiration dates.
Bidirectional tracking: allows devices to be linked to specific patients and records which professional assigned them.
Control in laboratories and pharmacies: ensures proper identification of medicines, samples, and clinical results.
Retail
Price and product information management: ensures accuracy in the information available to consumers and sales systems.
Real-time inventory control: optimizes stock levels and improves restocking and delivery times to the end customer.
Global product traceability: tracks goods from the country of origin to delivery at the point of sale.
Operational efficiency in logistics: improves order preparation, transport, and goods reception.
Continue your learning in EDI and Compliance!
Webinars, Success Stories, Guides, Reports… Here you will find all our premium content.


